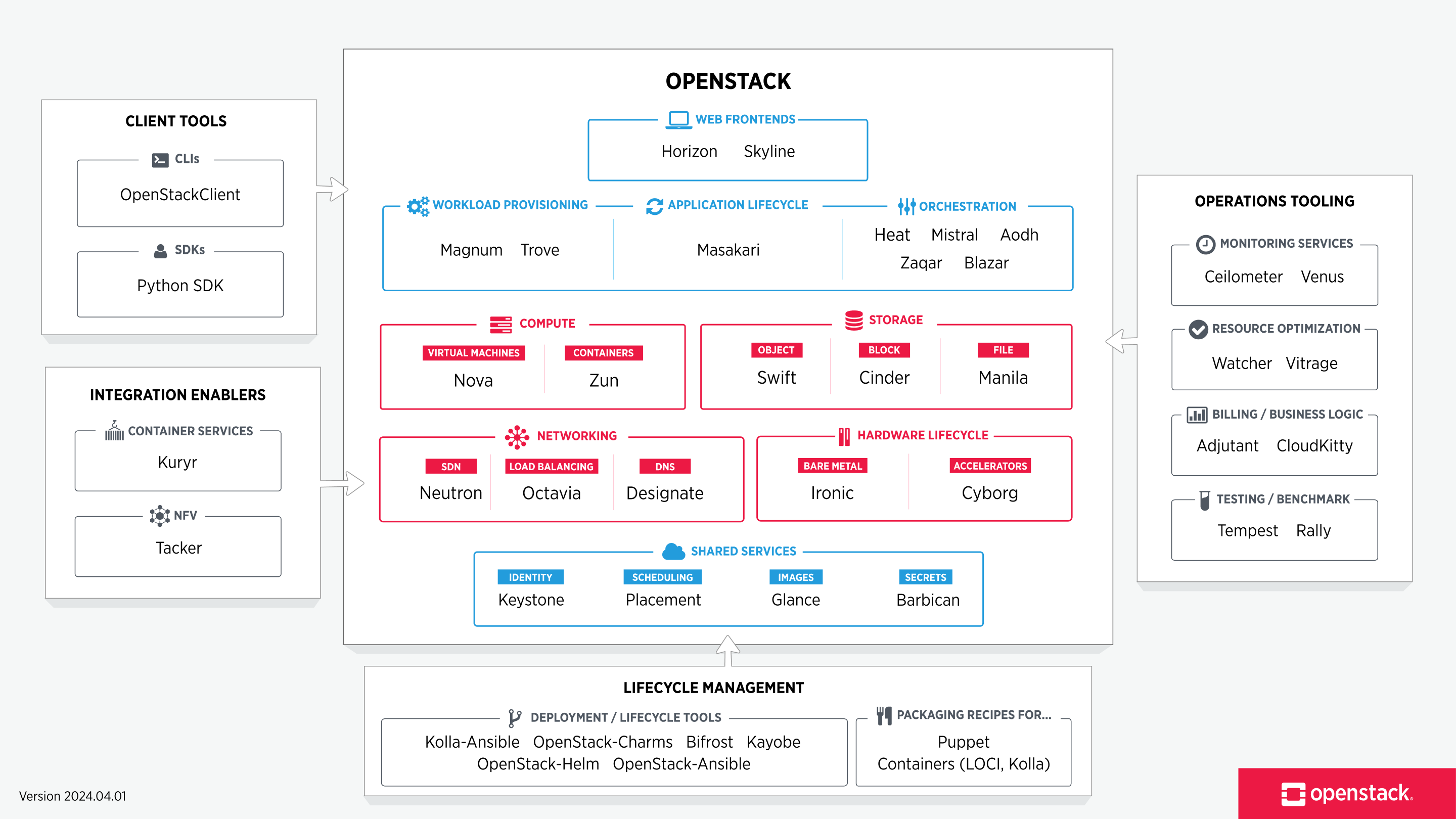
Open Stack Platform in a glimpse… !!



top, htop, or mpstatuptime or check the output of top (the three numbers at the top-right).nproc).top or ps -eo pid,ppid,cmd,%mem,%cpu --sort=-%cpu.free -h or vmstat -s.free -h or swapon -s).top or ps -eo pid,ppid,cmd,%mem --sort=-%mem.df -h to check disk usage across filesystems.df -i to check inode utilization.iostat, iotop, or dstat./var/log/ for any disk-related errors.iftop, ip -s link, or netstat.ss or netstat to check open connections and ports.ping, traceroute, or mtr.vnstat, iftop, or nload.journalctl or /var/log/syslog (for system-wide events).dmesg or journalctl -k to check for hardware errors or warnings.uptime command provides server uptime and load averages.sar or atop.systemctl status <service> or service <service> status.ps aux | grep Z to list zombie processes.who, w, or last./var/log/secure or /var/log/auth.log.iptables -L or ufw status.ss -tuln or netstat -tuln.sensors (part of lm-sensors package).mdadm or vendor tools if RAID is configured.crontab -l or check /etc/crontab./var/log/syslog for cron-related logs.top, df, iostat, and log parsing can provide quick insights.By periodically reviewing these parameters, you can ensure the Linux server’s health and address potential issues proactively.
SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) is a modern approach to managing and optimizing wide area networks (WANs), allowing businesses to securely and efficiently connect remote offices, data centers, and cloud resources over the internet. Unlike traditional WANs, which rely on expensive, static MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) circuits or leased lines, SD-WAN uses software to dynamically manage the traffic across multiple types of network connections, such as broadband internet, 4G/5G, MPLS, and other network types.
Centralized Control Plane:
Decentralized Data Plane:
Traffic Management and Routing:
Application-Aware Routing:
Security:
Cloud Integration:
Simplified Management:
Cost Efficiency:
Improved Performance:
Scalability:
Flexibility:
Security:
Cloud Optimization:
Centralized Control and Visibility:
SD-WAN is revolutionizing the way organizations manage their WANs by using software to dynamically manage traffic, optimize application performance, and reduce costs. It provides a more flexible, secure, and efficient solution compared to traditional WAN architectures, making it particularly well-suited for modern cloud-driven, distributed enterprise environments.
“journalctl” – is a command-line tool in Linux used to query and view logs managed by the systemd-journald service, which is part of the systemd system and service manager. journalctl allows users to access log data from various sources in a consolidated, searchable format, covering everything from kernel and system logs to application logs for services that run on systemd.
Here’s a quick overview of how to use journalctl:
1 .View All Logs:
journalctl
2. View Most Recent Logs:
journalctl -r
3 .Follow Logs in Real-Time (similar to tail -f):
journalctl -f
4. Specify a Service:
journalctl -u [service-name]
5. Filter by Time:
journalctl –since “YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS” –until “YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS”
journalctl –since “1 hour ago”
6. Filter by Priority:
journalctl -p [priority]
7. View Kernel Messages:
journalctl -k
8. Advanced Filtering:
journalctl -u nginx –since “2024-10-01” –until “2024-10-31” -p warning